HTTP Methods and Forms
In web applications, HTTP methods define different behaviors of HTTP requests. For example, getting data from a server has a different method than sending data or deleting data. Here are the common HTTP methods.
Here’s a detailed markdown table that outlines common HTTP methods, their purposes, and typical use cases:
| HTTP Method | Purpose | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| GET | Retrieve data from a server | Fetching a webpage, retrieving user data |
| POST | Send data to a server to create a resource | Submitting a form, uploading a file |
| PUT | Update an existing resource or create if it doesn’t exist | Updating user information, replacing a resource |
| DELETE | Remove a resource from the server | Deleting a user account, removing a file |
| PATCH | Partially update a resource | Updating a single field in a user profile |
| HEAD | Retrieve headers only, without the body | Checking if a resource exists, getting metadata |
| OPTIONS | Describe the communication options for the target resource | Discovering allowed methods on a server |
You’ve already worked with the GET HTTP method many times, perhaps without even realizing it.
Make a Contact Page
We will make a contact page that receives contact data, validates it, and returns a message to the user. In the next lesson, we will store this information in a database. Optionally, you can send emails on form submission.
Which method do you think will be useful for receiving contact data via an HTML Form?
Answer: POST is probably best for this use case.
Make a contact page with an HTML Form that has the method="POST" for a post request and the action="/contact" attribute for sending that request to the /contact route and the ContactController (created below).
views/contact.tpl
{{ template "layout.tpl" . }}
{{ define "content" }}
<h2 class="text-2xl font-bold mb-4">Contact Us</h2>
<!-- notice the method="POST" for a POST request and the action specificying what route to hit. -->
<form method="POST" action="/contact">
<div class="form-control mb-4">
<label class="label">
<span class="label-text">Name</span>
</label>
<input type="text" name="name" placeholder="Your Name" class="input input-bordered" required />
</div>
<div class="form-control mb-4">
<label class="label">
<span class="label-text">Email</span>
</label>
<input type="email" name="email" placeholder="Your Email" class="input input-bordered" required />
</div>
<div class="form-control mb-4">
<label class="label">
<span class="label-text">Message</span>
</label>
<textarea name="message" placeholder="Your Message" class="textarea textarea-bordered" required></textarea>
</div>
<div class="form-control">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Send Message</button>
</div>
</form>
{{ if .Result }}
<div role="alert" class="alert mt-4 pe-8 w-fit">
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" fill="none" viewBox="0 0 24 24" class="stroke-info h-6 w-6 shrink-0">
<path stroke-linecap="round" stroke-linejoin="round" stroke-width="2" d="M13 16h-1v-4h-1m1-4h.01M21 12a9 9 0 11-18 0 9 9 0 0118 0z"></path>
</svg>
<span>{{ .Result }}</span>
</div>
{{ end }}
{{ end }}
Handling a different HTTP method other than GET is as simple as making a new handler in the controller.
controllers/default.go
// add to the bottom of the file
type ContactController struct {
beego.Controller
}
func (c *ContactController) Get() {
c.Data["Title"] = "Contact"
c.TplName = "contact.tpl"
}
// new: post handler
func (c *ContactController) Post() {
c.Data["Title"] = "Contact"
c.Data["Result"] = "Thank you for your submission!"
c.TplName = "contact.tpl"
}
routers/router.go
// add to the init() function
beego.Router("/contact", &controllers.ContactController{})
Try submitting your form, you should see something like this:
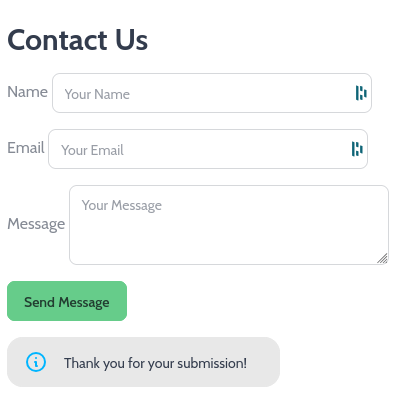
Handling Form Data on the Backend
Any form data that you send can match up with a struct that you define. Here is a struct that gets all the contact data.
type Contact struct {
Name string `form:"name"` // matches up with <input name="name" ...>
Email string `form:"email"` // matches up with <input name="email" ...>
Message string `form:"message"` // matches up with <textarea name="message" ...>
}
func (c *ContactController) Post() {
c.Data["Title"] = "Contact"
c.Data["Result"] = "Thank you for your submission!"
c.TplName = "contact.tpl"
// handle form data
contact := Contact{}
err := c.Ctx.BindForm(&contact) // Pass a pointer to the struct
if err != nil {
c.Data["Result"] = "ERROR: " + err.Error()
} else if contact.Message == "" || contact.Name == "" || contact.Email == "" {
c.Data["Result"] = "ERROR: Please enter all values."
} else {
// for now we will just log to the console.
log.Default().Println(contact)
}
}
Extra: Form Validation
See https://beegodoc.com/en-US/v2.0.x/validation/#examples for some more in-depth examples of form validation using Beego’s validation package.
Extra: Send an Email on Form Submission
Using the net/smtp package, you can send email. If you want, you can set up your own Gmail account with SMTP capabilities by following this guide. Alternatively, you can ask Mr. Buckley for credentials for a class account.
func (c *ContactController) Post() {
c.Data["Title"] = "Contact"
c.Data["Result"] = "Thank you for your submission!"
c.TplName = "contact.tpl"
// handle form data
contact := Contact{}
err := c.Ctx.BindForm(&contact) // Pass a pointer to the struct
if err != nil {
c.Data["Result"] = "ERROR: " + err.Error()
} else if contact.Message == "" || contact.Name == "" || contact.Email == "" {
c.Data["Result"] = "ERROR: Please enter all values."
} else {
// Send email
err = sendEmail(contact)
if err != nil {
c.Data["Result"] = "ERROR: Could not send email. " + err.Error()
} else {
c.Data["Result"] = "Email sent successfully!"
}
log.Default().Println(contact)
}
}
// sendEmail sends an email using SMTP
func sendEmail(contact Contact) error {
from := "my-email@gmail.com" // Replace with your email
password := "my-password" // Replace with your email password
toArr := [...]string{"recip1@gmail.com", "recip2@gmail.com"} // Replace with the recipient's email(s)
// slice the array
to := toArr[:]
// Set up authentication information.
auth := smtp.PlainAuth("", from, password, "smtp.gmail.com") // Replace with your SMTP server
// Compose the email message
subject := "New Contact Form Submission"
body := "Name: " + contact.Name + "\nEmail: " + contact.Email + "\nMessage: " + contact.Message
message := []byte("To: " + strings.Join(to[:], ",") + "\r\n" +
"From: " + from + "\r\n" +
"Subject: " + subject + "\r\n" +
"\r\n" + // This empty line separates the headers from the body
body)
// Send the email
err := smtp.SendMail("smtp.gmail.com:587", auth, from, to, message) // Replace with your SMTP server and port
return err
}
If you want your message to have HTML instead of plaintext, here is an example of the body and message variables.
body := "<b>Name: </b>" + contact.Name + "<br><b>Email: </b>" + contact.Email + "<br><b>Message: </b>" + contact.Message
message := []byte("To: " + strings.Join(to[:], ",") + "\r\n" +
"From: " + from + "\r\n" +
. "Subject: " + subject + "\r\n" +
"MIME-Version: 1.0\r\n" +
"Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8\r\n" +
"\r\n" + // This empty line separates the headers from the body
body)