HTTP and HTTPS
- How does the internet standardize data transfer?
- How do websites establish a secure connection for data transfer?
Creating a Self-Signed Local TLS Certificate with openssl
This certificate will be self-signed, meaning that it has not been validated by a third-party on the internet. This is for cases where yor computer does not have port 80 exposed to the public internet or you are doing local development.
Before running the following code, ensure you have openssl installed.
which openssl
This code creates a public and private key for the HTTPS protocol to use when encrypting your data.
sudo su - root
cd /etc/pki
mkdir -p nginx/private
cd nginx
# TODO: set this variable yourself to your hostname, like potato.potato
HOSTNAME=localhost
openssl req -x509 -out server.crt -keyout private/server.key \
-newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -sha256 \
-subj "/CN=$HOSTNAME" -extensions EXT -config <( \
printf "[dn]\nCN=$HOSTNAME\n[req]\ndistinguished_name = dn\n[EXT]\nsubjectAltName=DNS:$HOSTNAME\nkeyUsage=digitalSignature\nextendedKeyUsage=serverAuth")
# exit root user
exit
Uncomment these lines at the /etc/nginx/nginx.conf to enable SSL connection with your new certificate.
server {
listen 443 ssl;
listen [::]:443 ssl;
http2 on;
server_name _;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
ssl_certificate "/etc/pki/nginx/server.crt";
ssl_certificate_key "/etc/pki/nginx/private/server.key";
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
ssl_session_timeout 10m;
ssl_ciphers PROFILE=SYSTEM;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
# include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
}
Test the nginx configuration to see if it works and then apply changes by restarting.
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl restart nginx
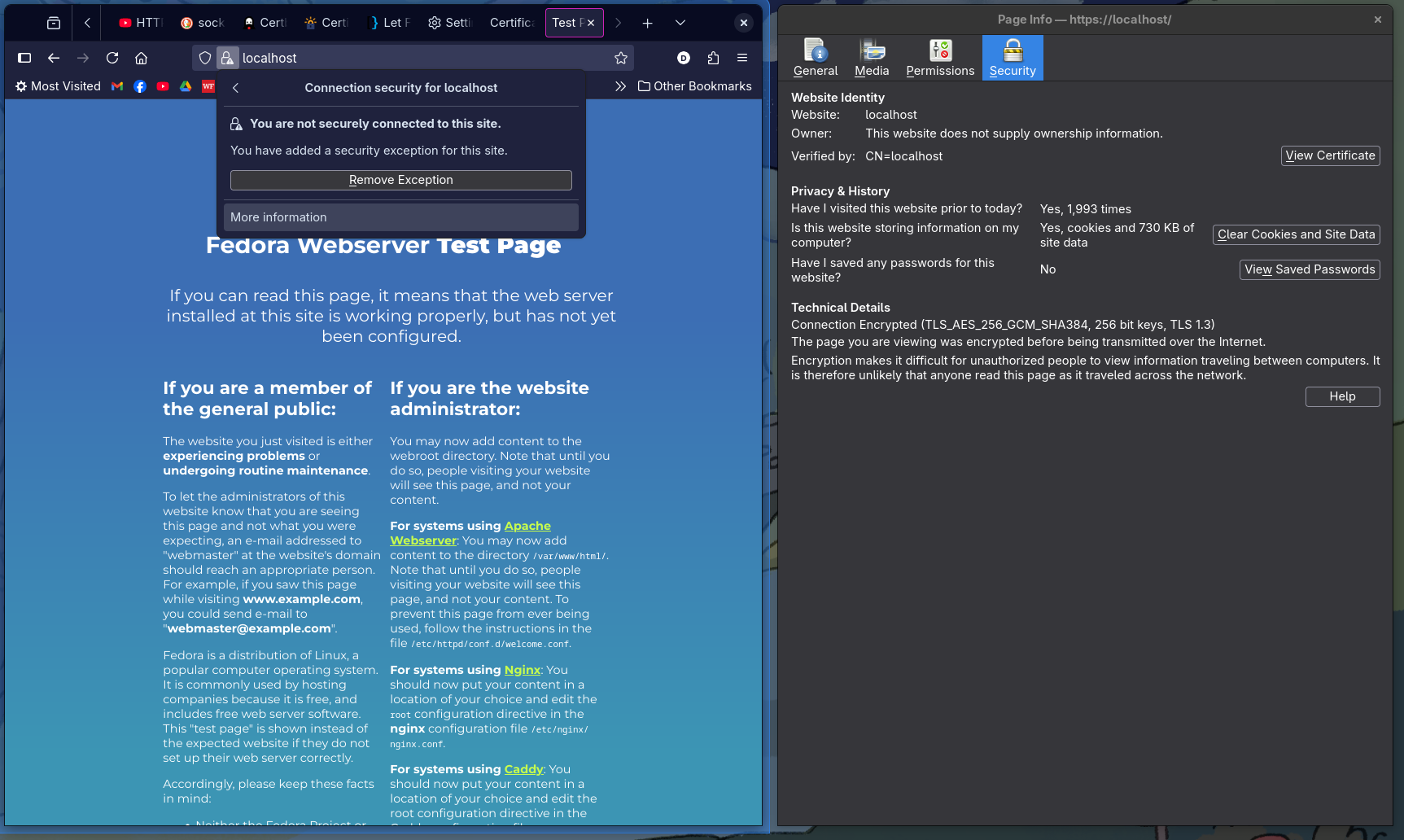
You should be able to access https://localhost in the browser. You will have to “accept the risk” of a self-signed certificate and continue. You can then see that you have an encrypted connection by looking at the “More Information” option in the browser.
Creating a TLS Certificate with Certbot and Let’s Encrypt
If you have a website available on the public internet (on port 80) and a domain name on public DNS, you can use certbot to create an SSL certificate with a free authority called “Let’s Encrypt”.
Don’t forget to open the right ports on the firewall.
sudo firewall-cmd --add-port 80/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --add-port 443/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Here is a great article on setting up certbot with nginx: https://dev.to/yousufbasir/setting-up-nginx-with-certbot-for-https-on-your-web-application-n1i for a public website.